Nonwoven Felts in Electric Vehicles: Improving Efficiency

The electric vehicle (EV) industry is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by advancements in battery technology, sustainability demands, and governmental pushes toward greener transportation. As manufacturers continue to refine the components that make EVs efficient and reliable, one often overlooked material is playing an essential role—nonwoven felts in electric vehicles. These materials, known for their versatility, durability, and thermal resistance, are becoming key components in the design and manufacturing of electric vehicles.
From thermal management in battery systems to acoustic insulation and lightweighting, nonwoven felts are integral to addressing the unique challenges presented by EV technology. This article explores how these materials are shaping the future of electric vehicle innovation.
Nonwoven Felts in Thermal Management for Electric Vehicles
One of the most critical challenges in electric vehicle design is managing the significant amount of heat generated by the lithium-ion batteries used to power these vehicles. Excessive heat not only reduces battery efficiency but also poses safety risks, such as thermal runaway, where overheating can lead to fire hazards.
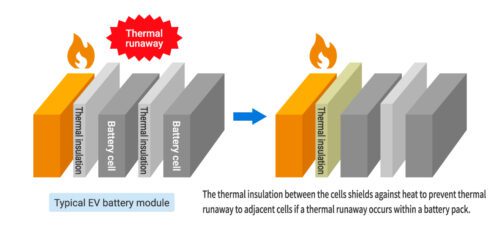
Nonwoven felts, particularly those infused with aerogels or other high-performance insulating materials, are playing a vital role in mitigating these risks. These felts are often used as thermal barriers between the battery cells, helping to control the heat generated during charging and discharging cycles.
Aerogel-Infused Nonwoven Felts for Battery Insulation
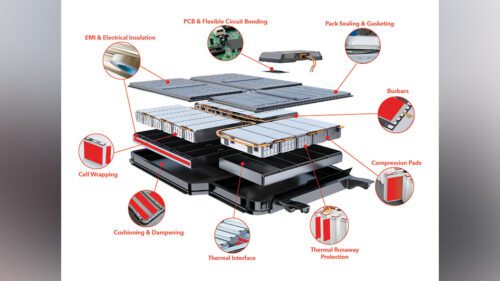
Aerogels are among the most effective insulating materials available today, known for their extremely low thermal conductivity. When combined with nonwoven felts, these materials create lightweight, flexible thermal barriers that can maintain the battery’s operating temperature within safe and efficient limits. This is particularly crucial as EVs push for longer ranges, requiring batteries to hold and discharge more energy without compromising safety.
Additionally, nonwoven felts help prevent thermal propagation—the spread of heat between cells—by acting as a barrier in the event of a single cell failure. This localized control of heat can reduce the risk of a total battery failure and extend the vehicle’s operational safety. Read more about managing thermal runaway in EV batteries.
Acoustic Insulation for Quieter EV Experiences
Another challenge that EV manufacturers face is the reduction of noise. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, which generate significant noise through the engine and exhaust system, EVs are nearly silent. While this is often marketed as an advantage, the absence of engine noise means that other, previously masked sounds, such as road noise, tire hum, and wind, become more noticeable.
Nonwoven felts in electric vehicles are well-suited to address these acoustic challenges. Their dense, fibrous structure makes them ideal for sound absorption. In EVs, nonwoven felts are being used in areas like:
- Interior cabin insulation: To minimize the transfer of external noise into the cabin.
- Underbody soundproofing: To dampen road and tire noise, improving passenger comfort.
- Engine bay and electric motor housing: While electric motors are quieter than traditional engines, they still generate high-frequency noise that can be disruptive. Nonwoven felts help dampen this sound effectively.
Incorporating nonwoven felts into EV designs for acoustic management not only enhances the driving experience but also helps manufacturers meet increasingly stringent noise regulations, particularly in urban environments.
Lightweighting with Nonwoven Felts in Electric Vehicles
One of the most important goals for EV manufacturers is reducing the overall weight of vehicles. Lighter vehicles are more energy-efficient, which directly translates into longer driving ranges—a key factor in consumer acceptance of EV technology. Nonwoven felts in electric vehicles offer a versatile, lightweight solution for a variety of applications where traditional materials would add unnecessary bulk.
Replacing Traditional Insulation Materials
In conventional vehicles, materials such as heavy foam or plastic-based insulation are commonly used for thermal and acoustic management. However, these materials add weight, which can reduce fuel efficiency or, in the case of EVs, limit the vehicle’s range. Nonwoven felts, on the other hand, provide comparable or better performance at a fraction of the weight.
Lightweight Heat Shields

Nonwoven felts are also used in lightweight heat shields for electric motors and battery components. These materials offer the required thermal protection without the weight penalty associated with metal heat shields. This is especially important as manufacturers push the boundaries of EV performance, where weight savings can significantly impact range and efficiency.
Sustainability and Recyclability of Nonwoven Felts
As the world shifts towards more sustainable practices, the recyclability and environmental footprint of materials used in manufacturing are becoming increasingly important. Nonwoven felts, especially those made from recycled fibers or natural materials, offer a more sustainable alternative to traditional insulation and structural components.
EV manufacturers are under pressure to not only reduce the emissions of their vehicles but also to lower the environmental impact of their entire production process. By incorporating nonwoven felts, manufacturers can contribute to a circular economy, where materials are reused and recycled, reducing the overall demand for virgin materials.
BIT’s nonwoven felts, for example, are produced using efficient manufacturing techniques that minimize waste and energy consumption, aligning with the broader goals of the electric vehicle industry to create more sustainable products.
Future of Nonwoven Felts in EV Applications
As electric vehicle technology continues to evolve, so too will the applications for nonwoven felts. Future innovations may include:
- Advanced thermal management systems: Nonwoven felts combined with phase change materials (PCMs) or smart textiles that actively respond to temperature changes.
- Enhanced acoustic solutions: Felts that incorporate nanotechnology or smart fibers to further enhance sound absorption and noise-canceling properties.
- Bio-based nonwoven felts: As sustainability becomes an even greater focus, bio-based and biodegradable nonwoven felts will likely play a larger role in EV manufacturing.
The versatility, lightweight properties, and superior insulation capabilities of nonwoven felts make them an essential material in the ongoing innovation of electric vehicles. From increasing range to improving safety and comfort, these materials will continue to be a crucial part of the EV revolution.
Conclusion
As the electric vehicle market accelerates, nonwoven felts are poised to become even more integral to vehicle design and performance. Their ability to provide superior thermal management, noise reduction, and lightweight construction makes them ideal for addressing the unique challenges of EV technology. By leveraging the benefits of nonwoven felts, manufacturers can improve the efficiency, safety, and sustainability of their vehicles, driving the future of transportation towards a greener, more innovative horizon.

