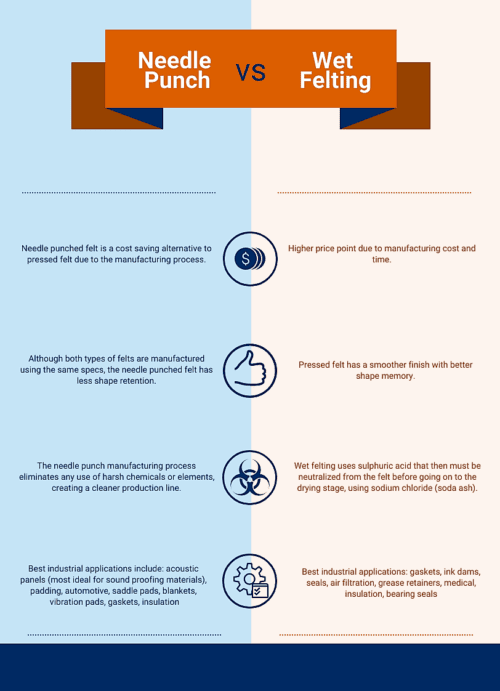
Natural Fiber Nonwoven Felts: Eco-Friendly Applications Across Industries
As industries demand more eco-friendly and natural materials, natural fiber nonwoven felts are gaining traction across various sectors. At Bouckaert Industrial Textiles (BIT), we focus on producing high-performance needle-punched felts from 6 oz per square yard and up. Our felts meet the growing demand for sustainability while maintaining quality.
Explore how natural fiber nonwoven felts, including wool, rayon, jute, hemp, and cotton, are transforming industries from automotive to agriculture.
1. Wool Felts: Natural Fiber, Eco-Friendly, and Durable

Wool felts have natural properties like insulation, moisture-wicking, and flame resistance, making them a go-to solution across industries. Their ability to absorb sound, insulate against heat, and resist fire make wool felts a sustainable choice for both industrial and residential applications.
A. SAE/Buzz, Squeak, and Rattle (BSR) Applications

In the automotive industry, wool felts are used in BSR testing to reduce friction and dampen vibrations. This reduces wear and tear on mechanical parts, enhancing durability and sustainability. Automakers use wool felts in sensitive areas like door panels and instrument clusters to reduce noise, contributing to a quieter and more comfortable driving experience.
B. Equestrian Saddle Pads
Wool felts are widely used in saddle pads to provide comfort, moisture control, and insulation for horses and riders. Wool’s moisture-wicking properties help keep the horse’s back dry, and its natural cushioning reduces pressure points, making it a superior material for equestrian equipment.
C. Mattress and Furniture Padding

Wool felts are used in the mattress and furniture industries for padding and flame protection. Wool’s natural flame retardancy makes it a safer choice compared to synthetic materials. Its breathability and softness provide added comfort, which is why it’s increasingly being used in luxury mattresses and eco-friendly furniture designs.
In the furniture industry, wool felts are used as padding in chairs, sofas, and upholstered goods. With consumers demanding more sustainable furniture options, wool’s renewable and biodegradable qualities make it an attractive alternative to synthetic foams.
D. Undercarpet Padding
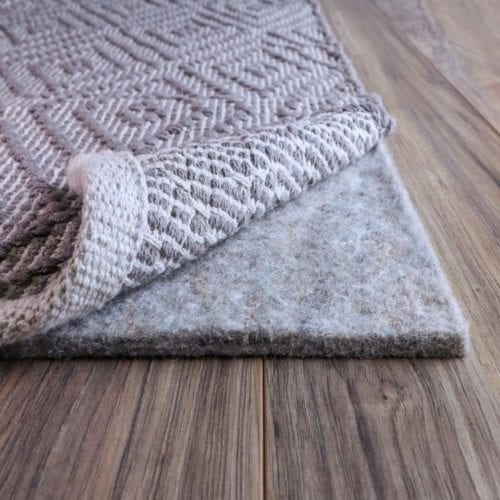

For interior applications, wool felts serve as under-carpet padding, offering noise reduction and comfort while being naturally fire-resistant. Wool’s durability ensures that carpets last longer and provide better insulation, both thermal and acoustic.
E. Acoustic Panels and Batts for Office Interiors
BIT is pushing into the market for wool acoustic panels and batts in office interiors, providing sustainable sound insulation for modern workspaces. Wool’s natural sound absorption and flame retardancy make it ideal for open-plan offices and meeting rooms. As businesses seek quieter, more productive environments, sustainable materials like wool are gaining popularity in interior design.
In green building projects, wool is increasingly being used for acoustic panels and insulation. Its ability to regulate temperature and absorb noise makes it an excellent material for reducing energy consumption and improving workplace comfort.
2. Rayon Felts: Versatile Natural Fiber Solutions
Rayon felts offer excellent sustainability and performance for a range of industries. Derived from natural sources like wood pulp, rayon provides a renewable, biodegradable option for a variety of applications.
A. Hydroponic Growing Media
Rayon felts are increasingly used as growing media in hydroponic systems. These felts provide water retention and root support, making them ideal for urban and vertical farming. The ability to hold moisture while remaining lightweight makes rayon felts suitable for growing vegetables and herbs in controlled environments.
In hydroponic systems, where traditional soil is replaced by nutrient-rich water, rayon felts provide an essential structure for plant roots to thrive. Rayon’s biodegradable nature ensures that it doesn’t leave behind harmful waste, making it an ideal solution for environmentally conscious urban farms.
B. Medical and Orthopedic Uses
Rayon felts are used in medical dressings and orthopedic padding for their softness, absorbency, and biodegradability. In the medical industry, rayon felts are used in wound care products, such as bandages, where their softness and moisture retention help promote healing.
In orthopedic applications, rayon felts provide cushioning for devices like prosthetics and braces. The ability of rayon to conform to the body and its hypoallergenic properties make it a superior material for sensitive medical uses. Its biodegradability ensures that it reduces environmental impact once discarded.
3. Cotton Felts: Sustainable Natural Fiber for Padding
Though not a focus at BIT due to flammability issues, cotton felts, including recycled shoddy, are still a popular natural fiber option across industries. Cotton, particularly recycled cotton, is being used more frequently in the furniture and bedding industries as consumers demand more eco-friendly options.
A. Mattress and Furniture Padding
Recycled cotton felts are widely used in the mattress and furniture industries for padding. Offering a more sustainable alternative to synthetics, cotton felts provide comfort and breathability. Recycled cotton (often referred to as shoddy) is made from post-consumer denim and other fabrics, giving it a second life as padding material.
In mattresses, cotton felts serve as a cushioning layer that also helps regulate temperature. In furniture, these felts are often used in upholstery, contributing to more eco-conscious designs without sacrificing comfort or durability.
B. Insulation from Recycled Denim
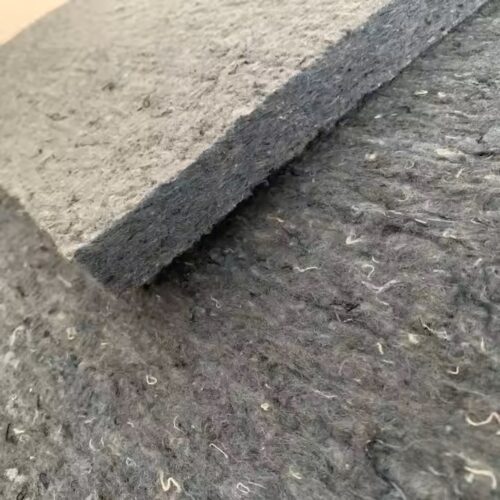

Recycled cotton felts (shoddy), especially from denim, are used as thermal and acoustic insulation in eco-friendly construction projects. Denim-based felts are highly effective at absorbing sound and regulating heat, making them ideal for use in walls, floors, and ceilings in sustainable buildings.
4. Jute and Hemp: Natural Fibers for Automotive and Packaging
Jute and hemp fibers are becoming prominent in the automotive industry and for sustainable packaging. These bast fibers offer strength, flexibility, and biodegradability, making them ideal for applications where synthetic materials might otherwise be used.
A. Automotive Molded Parts and Acoustics
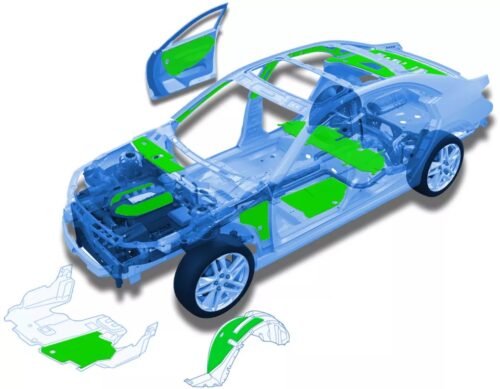
Jute and hemp fibers are increasingly used in the automotive industry for molded parts and acoustic insulation. These fibers provide lightweight yet durable solutions for door panels, trunk liners, dashboards, and other internal components. The stiffness and strength of jute and hemp make them ideal for producing moldable, environmentally friendly parts that maintain structural integrity under stress.
Hemp and jute are also effective in reducing cabin noise, contributing to a more comfortable driving experience. Automakers are looking for alternatives to petrochemical-based products, and bast fibers are offering a sustainable solution without compromising performance.
B. Eco-Friendly Packaging and Insulation
Jute and hemp are used in eco-friendly packaging and insulation, offering biodegradable and cost-effective alternatives for various industries. As packaging materials, they provide cushioning and support, while also being compostable at the end of their lifecycle.
C. Agricultural Textiles
Hemp and jute felts are used in agricultural textiles for erosion prevention and weed control. These materials decompose into the soil and enrich it with organic matter. Jute and hemp-based textiles are ideal for use in landscaping, farming, and other outdoor applications where biodegradability is a key concern.
5. Additional Applications for Natural Fiber Nonwoven Felts
Natural fiber nonwoven felts are also used in niche applications, such as:
- Soundproofing in Green Buildings: Wool, rayon, and cotton felts are used for soundproofing walls in sustainable construction projects.
- Protective Packaging for Fragile Goods: Wool and cotton felts are used to protect fragile items like electronics and glass during shipping. These materials provide cushioning without relying on plastic or foam.
Conclusion: The Future of Natural Fiber Nonwoven Felts
At Bouckaert Industrial Textiles, we are committed to producing high-quality, eco-friendly natural fiber nonwoven felts to meet the growing demand for sustainable materials. From wool felts used in automotive and equestrian applications to rayon felts supporting hydroponic agriculture, we ensure our materials contribute to a greener future.
As industries continue to innovate and search for greener solutions, natural fibers like wool, rayon, and hemp will play a crucial role in providing durable, eco-friendly felts for a wide range of applications.
Read more about natural fiber uses in sustainable applications here.
Learn more about our SAE Felts on our product page.